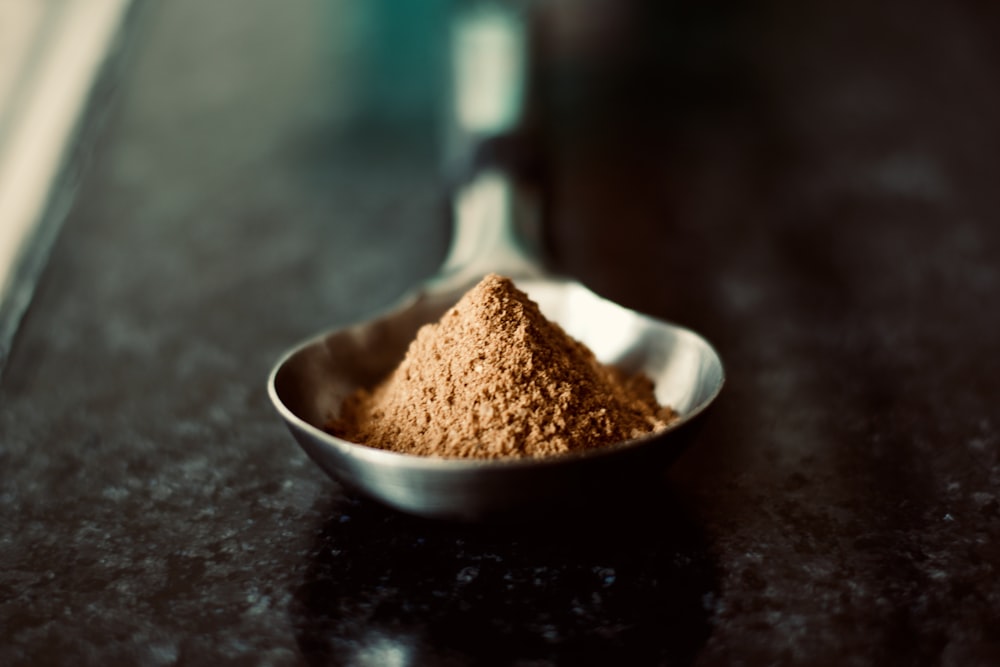
For a long time, cacao—the main component in chocolate—has been lauded for both its cultural importance and its rich flavour. Cacao has long been admired for its decadent flavour, but new research and anecdotal evidence suggest it may contain chemicals that cause psychedelic effects. This has led to a renewed interest in this plant.
Cacao, a spice often used in baked goods and hot drinks, actually comes from a tree in the tropical woods of South and Central America called Theobroma cacao. Cacao was considered a holy elixir by the ancient Aztecs and Mayans, who believed that drinking it during religious rituals bestowed magical powers.
Scientific investigations in recent decades have illuminated cacao’s rich chemical makeup, illuminating a web of chemicals with functions far beyond that of flavour and fragrance alone.
Theobromine, caffeine, and anandamide are the most prominent of these chemicals; they are all recognised for their ability to affect mood and cognition and even produce subtle changes in consciousness.
In this article, we’ll take a look at cacao from every angle: its fascinating history, the chemical components that give it its psychedelic properties, and the new studies that are trying to figure out how it affects our minds.
Come with us on a sensory adventure as we peel back the layers of cacao’s charm, discovering more than just a tasty snack—we could be uncovering the interesting potential that it is a subtle but enchanting psychoactive chemical.
Is Cacao A Psychoactive Substance?
There are several psychotropic chemicals in cacao, however, they are typically less intense than those of caffeine or THC (marijuana). The main ingredients in cocoa that produce intoxicating effects are:
- Theobromine: This stimulant is related to caffeine and is found in varying amounts in cacao. Theobromine can have a mild stimulating effect on the central nervous system, leading to increased heart rate and feelings of alertness.
- Caffeine: While present in lower amounts compared to coffee, cacao does contain some caffeine. This well-known stimulant can contribute to increased energy and improved mood.
- Anandamide: Often referred to as the “bliss molecule,” anandamide is a cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to the same receptors as THC in the brain. It’s found in small amounts in cacao and may contribute to the mood-enhancing effects associated with chocolate consumption.
- Phenylethylamine (PEA): Known as the “love molecule,” PEA is a natural compound found in chocolate and is associated with feelings of euphoria and attraction. However, its effects are typically short-lived.
The psychedelic effects of cacao are typically thought to be modest, even though each of these chemicals has its own set of effects. Although they are not likely to cause extreme or hallucinatory experiences, they can help enhance feelings of pleasure and well-being.
Keep in mind that ingredients like these can be found in chocolate in varying proportions depending on things like the cacao bean variety, processing techniques, and the final product.
Does Chocolate Have Psychoactive Effects?
Cacao, the primary ingredient in chocolate, has several chemicals that are responsible for its intoxicating properties. Stimulants theobromine and caffeine bring heightened awareness and a mild improvement in mood.
A compound called anandamide, which is popularly known as the “bliss molecule,” binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and may cause tranquillity and joy. One other thing: phenylethylamine, the “love molecule,” might make you feel slightly euphoric.
The effects of these psychoactive components in chocolate are not as strong as those of more powerful narcotics, although they are still present. The cultural and historical importance of chocolate, along with the interaction of various components, makes our enjoyment of this wonderful food even more nuanced.
While opinions may differ, many find that eating chocolate fills them with joy in a way that transcends taste and stimulates their senses and thoughts.
Additionally, chocolate’s psychedelic effects go beyond the short-term physiological consequences. A lot of people identify chocolate with happy times, celebrations, and comfort, so there are emotional and cultural connections at work here. Savouring a piece of chocolate may increase the feel-good effect by releasing endorphins.
In addition to its current worldwide popularity, chocolate’s long and storied history—beginning with its religious use in ancient Mesoamerican civilizations—only adds to its charm.
The distinctive profile of mental effects associated with chocolate eating is due in large part to the synergistic interplay of the psychoactive compounds found in chocolate, which are often present in lesser concentrations compared to coffee’s caffeine.
As a result of chocolate’s careful balancing act between its stimulants and relaxants, it can induce a state of euphoria and calm at the same time.
What Are The Mental Effects Of Cacao?
For the most part, cocoa has modest and subjective mental impacts. Anandamide, theobromine, caffeine, and phenylethylamine are among the chemicals thought to be responsible for these actions. A few of the possible psychological impacts of eating chocolate are as follows:
- Mood Enhancement: Cacao contains compounds like theobromine and anandamide, which may contribute to a sense of well-being and mood elevation. Some people report feeling happier or more relaxed after consuming chocolate.
- Increased Alertness: The presence of theobromine and caffeine in cacao can have mild stimulant effects, leading to increased alertness and improved focus. However, the amounts of these stimulants in chocolate are generally lower compared to other sources like coffee.
- Mild Euphoria: Phenylethylamine, known as the “love molecule,” is present in chocolate and is associated with feelings of euphoria. However, its effects are typically short-lived.
- Relaxation: Despite its stimulant content, cacao also contains compounds that may have relaxing effects. The combination of stimulants and relaxants can result in a balanced, subtle impact on mental state.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Some studies suggest that the flavonoids present in cacao may have cognitive benefits, including improved memory and increased blood flow to the brain. These effects are more long-term and may be associated with regular, moderate consumption.
It’s worth noting that various people have different reactions to cacao; the mental consequences might be different depending on things like the kind of chocolate, how much is eaten, and how sensitive one is to stimulants.
Although cacao contains psychoactive substances, they are typically perceived as having a mild and pleasant effect rather than being extremely strong or hallucinatory. Caution is essential, as is consideration of one’s tolerance when consuming this or any meal or drink.
Conclusion
Theobromine, caffeine, anandamide, and phenylethylamine are some of the substances found in cacao that give it modest psychedelic characteristics. Mood elevation, heightened alertness, mild euphoria, relaxation, and perhaps cognitive advantages are some of the mental effects that result from these components.
The enjoyment you get from eating chocolate is enhanced by these effects, which are usually mild but welcome.
Cacao has a rich history that extends beyond its culinary uses, and its cultural significance has given it an air of mystery that has fascinated people ever since it was first used by ancient cultures like the Mayans and the Aztecs.
As we delve more into the mysteries of cacao, we discover that this beloved plant provides a complex web of chemicals that affect our mood in addition to a wealth of delightful sensory experiences.
Individual reactions to cacao can differ, and it’s important to exercise moderation, as is the case with any psychoactive substance. Although the intoxicating effects of cacao on the mind are not as strong as those of stronger hallucinogens or stimulants, they do add to the allure and charm of this traditional treat.
Delving into the psychological impacts of cacao brings an intriguing new angle to our comprehension of the intricate interplay among cuisine, society, and the human psyche.
For more information, read this guide “cacao psychoactive”.